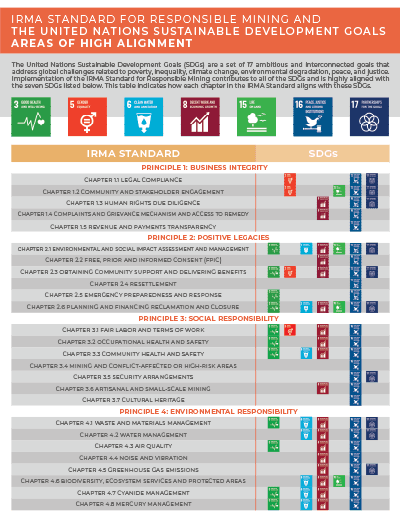
 The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 ambitious and interconnected goals that address global challenges related to poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace, and justice. Implementation of the IRMA Standard for Responsible Mining contributes to all of the SDGs and is highly aligned with the seven SDGs listed below. This page indicates how each chapter in the IRMA Standard aligns with these SDGs.
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 ambitious and interconnected goals that address global challenges related to poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace, and justice. Implementation of the IRMA Standard for Responsible Mining contributes to all of the SDGs and is highly aligned with the seven SDGs listed below. This page indicates how each chapter in the IRMA Standard aligns with these SDGs.
About the UN Sustainable Development Goals
In 2015 the United Nations (UN) Member States unanimously adopted the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, including the 17 SDGs and 169 underlying targets. The targets under each SDG clarify how progress can be measured and how the Goals can be reached. The UN Member States aim to achieve the SDGs, also known as the “Global Goals,” by 2030.
 The current “Decade of Action” to achieve the SDGs calls for accelerating action that extends far beyond government actors. The SDGs can only be met by 2030 with the active engagement of companies—including mining companies and their suppliers; consumers; communities; civil society organizations; and others.
The current “Decade of Action” to achieve the SDGs calls for accelerating action that extends far beyond government actors. The SDGs can only be met by 2030 with the active engagement of companies—including mining companies and their suppliers; consumers; communities; civil society organizations; and others.
IRMA’s Contributions to SDG Achievement
Implementation of the IRMA Standard for Responsible Mining contributes to all of the SDGs. Read A Comparative Analysis of the SDGs and the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance Standard for Responsible Mining for the whole story.
Of the 17 SDGs, the IRMA Standard is highly aligned with seven identified in the summary chart at right (click the chart for a full size pdf).
Below, a section is dedicated to each of those seven SDGs.
Good Health and Well Being - SDG 3
SDG 3 aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages by 2030. This Goal intends to end HIV/AIDs, tuberculosis, and malaria and reduce hepatitis, water-borne illnesses, and other infectious diseases. It calls for a reduction in child and maternal mortality rates, universal access to healthcare and essential medicines, and a substantial reduction in the number of deaths from health risks such as hazardous chemicals and contamination of the air, water, and soil.
Under the IRMA Standard, mining companies must advance the health and well-being of communities and take measures to prevent and eradicate the spread of disease. This is accomplished through a range of mechanisms required under the IRMA Standard, including but not limited to: Environmental and Social Impact Assessment and related impact management plans; health and safety management systems—both on company and community levels; responsible management of mine waste materials; and monitoring and managing impacts of a project on water quality and quantity.
Read A Comparative Analysis of the SDGs and the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance Standard for Responsible Mining for the whole story.
Gender Equality - SDG 5
SDG 5 aims to achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls by 2030. Goal 5 calls for an end to all discrimination against women and girls, the elimination of gender-based violence, and full and effective participation and equal opportunities for leadership for women in all levels of political, economic, and public life.
The IRMA Standard fosters inclusivity and empowerment of women on many levels, and specifically notes that mining companies are to remove barriers to engagement for women. The Standard calls on companies to obtain and maintain broad community support for mining projects, based on meaningful input by all affected community members, including women. The Standard requires operating companies to take measures to prevent and address harassment, intimidation, and/or exploitation, especially in regard to female workers. Operating companies are also required to provide maternity leave; where there is no national law nor collective bargaining agreement, the maternity leave must be no less than 14 weeks.
Read IRMA Fact Sheet: Gender Equality and Gender-Based Protections in the IRMA Mining Standard.
Clean Water and Sanitation - SDG 6
SDG 6 aims to ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all by 2030. Goal 6 intends to achieve universal and equitable access to safe drinking water for all. This includes reducing waste and pollution in waterways and reducing the dumping of hazardous chemicals and materials. This calls for developing strategies for the protection and restoration of water-related ecosystems and the expansion of water conservation infrastructure in developing countries.
The IRMA Standard includes extensive requirements regarding water quality and sanitation. Requirements include but are not limited to environmental and social impact assessment and related management plans; identification of water users, water rights holders, and other stakeholders potentially affected by mine water management practices; collaboration with relevant stakeholders to identify current and future uses of water at the local and regional level that may be affected by the mine’s water management practices; and mine closure plans that include comprehensive requirements to prevent the degradation of water resources and to maintain water management, water treatment, and mine site and waste site geotechnical stabilization, with adequate related financial assurance.
The IRMA Standard calls on operating companies to implement best practice water and waste management methods to avoid long-term treatment. Where a decision is made to proceed with long-term water treatment, the operating company must take all practicable efforts to minimize the volume of water to be treated.
Read A Comparative Analysis of the SDGs and the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance Standard for Responsible Mining for the whole story.
Decent Work and Economic Growth - SDG 8
SDG 8 promotes sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all by 2030. Goal 8 calls for policies that promote sustained economic growth, job creation, creativity and innovation, and entrepreneurship. It also calls for the eradication of forced labor, an end to human trafficking, and elimination of the worst forms of child labor. It aims to protect labor rights and promote safe working environments for all workers, including women and migrant workers, and those engaging in precarious employment. It endeavors to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation.
The IRMA Standard incorporates extensive requirements for labor rights, including the rights of workers to freedom of association and collective bargaining, and requires mining companies to pay a living wage or better. Furthermore, the Standard requires that children (persons under the age of 18) shall not be hired to do hazardous work and sets a minimum age requirement of 15 for non-hazardous work. The Standard expressly prohibits employment of forced labor or participation in human trafficking.
Read A Comparative Analysis of the SDGs and the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance Standard for Responsible Mining for the whole story.
Life on Land - SDG 15
SDG 15 aims to protect, restore and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and revers land degradation and halt biodiversity loss by 2030. Goal 15 is focused on the conservation, restoration, and sustainable use of freshwater and mountain ecosystems and encourages urgent action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats. It promotes sustainable management plans to prevent forest degradation, combat desertification, and mobilize resources to finance forest conservation and reforestation. It also encourages the conservation of biodiversity.
The IRMA Standard’s requirements for environmental and social impact assessments and related management plans promote achievement of this Goal. In particular, the Standard requires operating companies to prepare a reclamation and closure plan that demonstrates how affected areas will be returned to a stable landscape with an agreed post-mining end use. Among other minimum requirements, the reclamation and closure plan must include stabilization and final topography of the reclaimed mine lands; topsoil salvage to the maximum extent practicable; and topsoil storage in a manner that preserves its capability to support plant regeneration.
When addressing revegetation and ecological restoration as required in the IRMA Standard, companies must prioritize native species as appropriate for the agreed post-mine land use and provide quantitative revegetation standards with clear measures to be implemented if the standards are not met within a specified time. Companies must also set a defined period, no longer than 10 years, when planned revegetation tasks shall be completed; measures for control of noxious weeds; and planned activities to restore natural habitats, as well as biodiversity, ecosystem services, and other conservation values.
Read A Comparative Analysis of the SDGs and the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance Standard for Responsible Mining for the whole story.
Peace, Justice, and Strong Institutions - SDG 16
SDG 16 aims to promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels by 2030. Goal 16 advocates for a reduction of violence in all forms, including human trafficking and violence against children. It calls for representative, responsive, and participatory governance that is inclusive at all levels. Institutions should be effective, accountable, and transparent. Fundamental freedoms should be protected, and non-discriminatory laws and policies for sustainable development should be promoted.
The IRMA Standard provides extensive requirements related to this Goal, only some of which are discussed here. The Standard prohibits hiring children to do hazardous work and hiring children under the age of 15 to do non-hazardous work. It also prohibits employment of forced labor and participation in human trafficking.
The Standard requires mining companies adopt a policy commitment that acknowledges its responsibility to respect all internationally recognized human rights. It also includes detailed requirements regarding respect for human rights in developing and implementing security measures. The Standard details requirements to follow international best practice when operating in conflict-affected or high-risk areas.
The Standard requires that mining companies utilize inclusive public engagement and participatory processes, all of which contribute toward peaceful and inclusive societies. At new and existing mines, the mining company must obtain Free, Prior and Informed Consent (FPIC) from Indigenous Peoples for proposed changes to mining-related activities that may result in new or increased impacts on Indigenous Peoples’ rights or interests. The mining company must also obtain and maintain broad community support, determined based on the opportunity for meaningful input by all potentially affected community members, including women, vulnerable groups, and marginalized community members, prior to any decision or resolution.
Furthermore, the operating company must develop culturally appropriate complaints and grievance procedures, aligned with the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights, including the need for the mechanism to be:
- Legitimate,
- Accessible,
- Predictable,
- Equitable,
- Transparent,
- Rights-compatible,
- A source of continuous learning, and
- Based on engagement and dialogue.
Read A Comparative Analysis of the SDGs and the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance Standard for Responsible Mining for the whole story.
Partnerships for the Goals - SDG 17
SDG 17 aims to strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development. Goal 17 acknowledges that progress on sustainable development requires strategic partnerships between governments, the private sector, and civil society at all levels—local, national, and international—across multiple disciplines. Data-sharing, policy coherence, and capacity-building are all areas in which increased collaboration can result in broader achievement toward all SDGs.
Mining companies are an important player in the global partnership for sustainable development. The IRMA Standard promotes a wide range of opportunities for mining companies to contribute to the SDGs through implementing and continuously improving responsible mining practices.
The IRMA Standard is particularly focused on mining’s impacts on affected communities and the environment where the mine operates. The Standard also includes extensive requirements for engagement and collaboration with affected communities, as well as development and implementation of plans for sharing benefits with communities. Furthermore, the Standard requires operating companies to collaborate with relevant stakeholders to identify current and potential future uses of water at the local and regional level that may be affected by the mine’s water management practices, and to identify and address shared water challenges and opportunities at the local and regional levels.
Read A Comparative Analysis of the SDGs and the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance Standard for Responsible Mining for the whole story.








